
Flatten The Curve, Load profiling
Load profiling
Refers to grouping customers based on their pattern of electric consumption over a given period of time. The time aspects can be considered from different perspectives:
Within the day: change of consumption behavior over the hours.
Example: a working family would have peak consumption in the morning and late afternoon with very low consumption during working hours. While a student may be classified as evening active and stable consumption during the day.
Within the week : different behavior on weekends.
Within the year: Different behavior according to time of the year. ( for example summer time versus the rest of the year)
How can this be used ?
- Targeted communication
Understanding consumption patterns can be a foundation stone for different grid management initiatives. By defining the main patterns, customers can be segmented according to these patterns. This segmentation process can be supported with other information such as ( type of the customer, type of house, volume of consumption). Subsequently, tailored communication strategies can be designed for each group.
- Tariffs Planning
Time of use tariffs, or TOUs, encourage customers to use energy when the demand is low “off-peak” by charging lower electricity prices for these hours. This will allow customers to reduce their electricity bills by shifting non urgent activities from peak, high price times to low peak/ price times. With introducing a smart home control system, customers would not even need to think about planning the non-urgent activities since these types of systems will decide the best time according to the price of electricity. Such activities include, for example; washing machines and electric car charging. Understanding consumptions’ patterns is a necessary step for designing efficient tariffs.
Practical Use Case
For the flexibility project in Utsira, we are interested to know different consumption patterns. Especially at the day time when there is energy production from solar panels.
Lower consumption at that time with high energy production can lead to voltage problems. Incentivizing customers to shift their consumption during that time can solve the problem. The mechanism for encouraging customers can be through time of use tariff or using the flexibility market.
Screening of domestic users and small businesses in Utsira gave us four distinct patterns.
.. 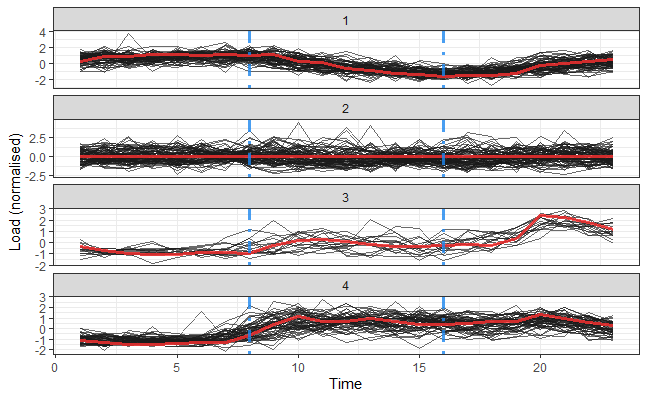
Group 1 : their consumption level is typically low in the time between 8 a.m to 18:00 pm
Group2 : they have no defined distinct pattern
Group 3: very low consumption during sleeping time, start to increase from 8 a.m and peak consumption after 20.00
Group 4: stable higher consumption starting from 10.00 until 23.00 than the rest hours.
It is important to notice that this profiling depends only on the shape of consumption and not the volume of consumption. Typically, consumption for each customer is normalized with an average of zero.
Implication
Group 2 and 4 exhibit flat profiles . These customers offer little scope for shifting electricity consumption during peak times. Consequently, a Time of Use may not be best successful for them.
In Utsira context, affecting the behavior of group 1 and 3 would be important to stabilize the network during times when there is high energy production from solar panels. Optimally, they would shift some of the activities that are done in the evening to the day.
Publisert